INTRODUCTION
Anorectal malformation (ARM) occurs in 1 in 5,000 neonates; rarely missed in boys, but can be missed in girls. ARMs are associated with other abnormalities including the VACTERL association, chromosomal abnormalities, duodenal atresia and oesophageal atresia
Missing ARM in a girl is usually a breach of duty
BOYS
- Figure 1: anus not present, rectum may have a fistula to the bulbar urethra, prostatic urethra or bladder neck
- Figure 2: anus not present, rectum opens via a fistula outside the muscle complex on the perineum

Figure 1: Anus is absent

Figure 2: Fistula opening onto scrotal raphe

Figure 3: ARM with a fistula to the urinary tract
- Once diagnosed boys should be kept nil-by-mouth, have an IVI and urgent transfer for surgery
GIRLS
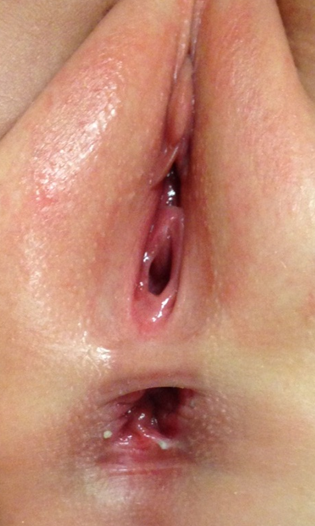
Figure 4:
- Normal urethra, vagina, perineal body, anus
- Anal opening in the muscle complex
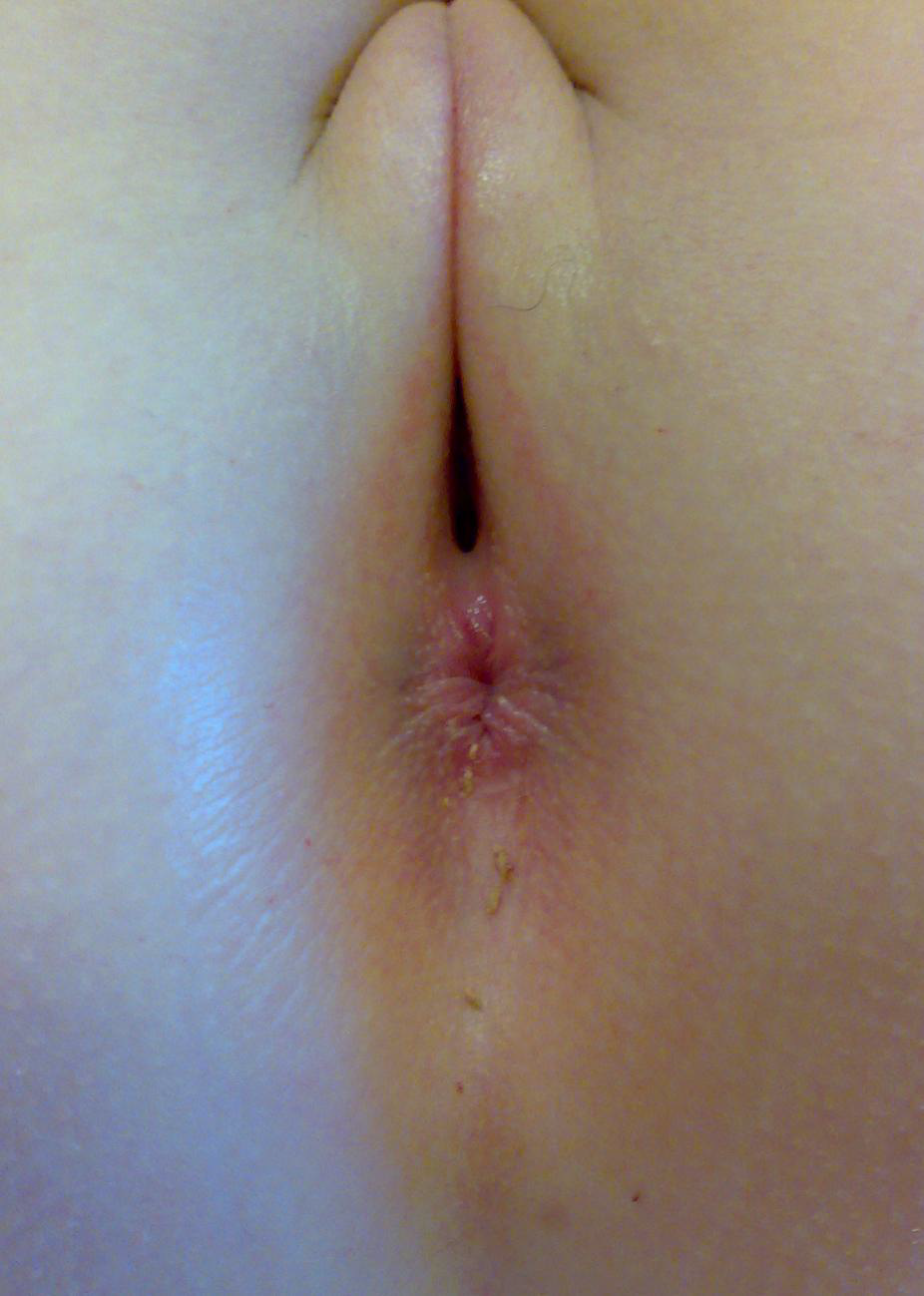
Figure 5:
- Anterior anus – extremely rare
- Opening of adequate size with muscle all around, but a very small perineal body
- No surgery required (requires routine referral)
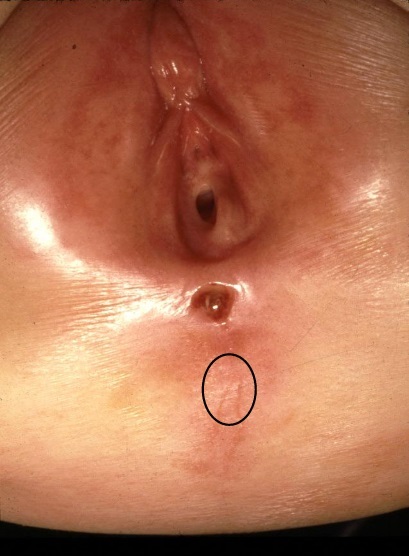
Figure 6:
- Recto-perineal fistula (muscle complex circled)
- Opening is a fistulous connection to the rectum – may not be adequate and is easily missed
- Surgery almost always indicated – refer urgently
- If obstructed, emergency surgery may be required
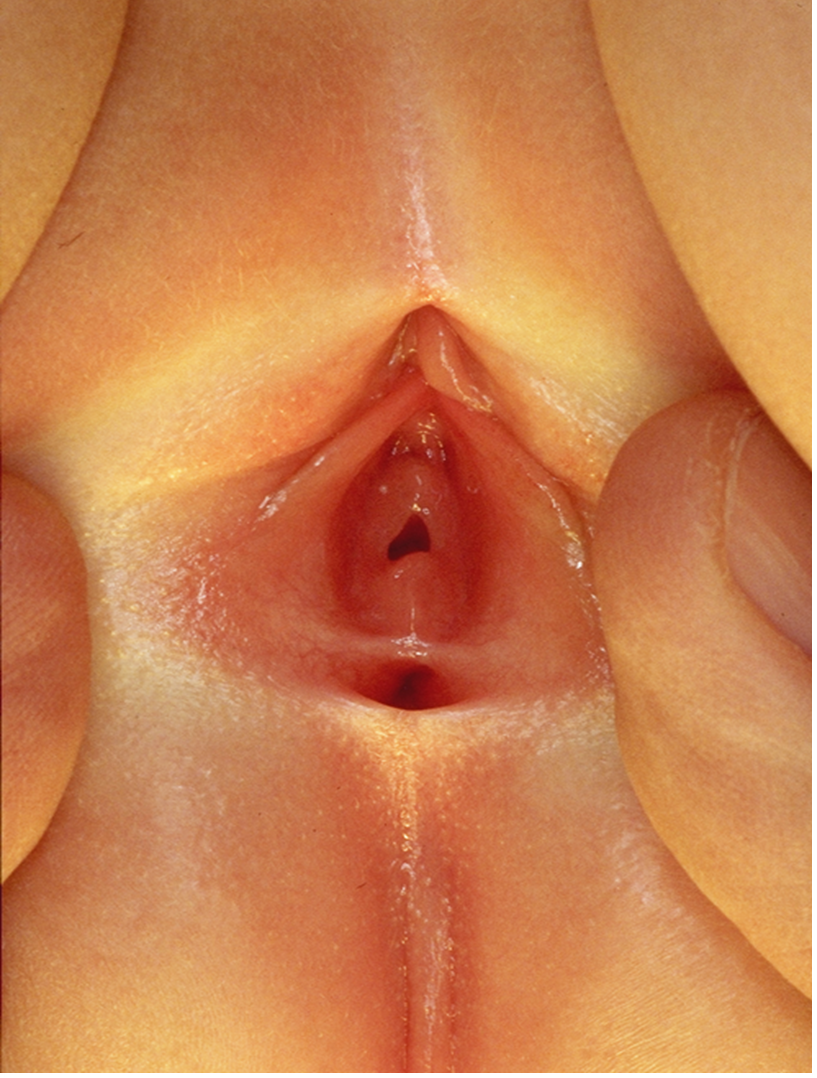
Figure 7:
- Recto-vestibular fistula
- Opening immediately behind the vagina
- No perineal body
- Emergency referral almost always required – opening will be insufficient to decompress the bowel
- More extreme but rare case of recto-vaginal fistula and cloaca should be identified at neonatal check
- Always check for ARM when:
- abnormal looking perineum
- delayed/no passage of meconium
- abdominal distension
- bilious vomiting
Non-urgent referral
- Most newborn girls with abnormal perineum require urgent referral; discuss with surgeon and see within a few days if:
- opening of adequate size to decompress the rectum and
- plenty of meconium being passed and
- no distension or vomiting
EXAMINATION
- Full physical examination
- look for:
- dysmorphic features
- cardiac anomalies
- limb anomalies
- abdominal distension
- describe the perineum
- look for:
Caution
- Presence of meconium in nappy does not exclude an ARM, as neonate may still pass meconium through a fistula
- Always clean the perineum and establish that a normally sited anus is present
MANAGEMENT
- Depends on size of any opening – see above
- If obstructed:
- nil-by-mouth, 8 Fr NGT, empty stomach by aspirating 4-hrly with a syringe and place NGT on free drainage by connecting to a bile bag
- Insert IV cannula and obtain blood for FBC, U&E, glucose and blood cultures
- Start maintenance IV fluids (see Intravenous fluid therapy guideline)
- Give broad spectrum antibiotics
- Give vitamin K IM (see Vitamin K guideline)
- Collect pre-transfusion bloodspot and send with baby to surgical centre
- Replace nasogastric losses mL-for-mL using sodium chloride 0.9% with 10 mmol potassium chloride in 500 mL IV
- Chest X-ray to confirm position of NGT, assess vertebral anomalies and cardiac outline
- Supine abdominal X-ray looking for dilated bowel/associated bowel atresia vertebral anomalies
- combined chest and abdominal X-ray is suitable as an alternative
- Take photographs of baby for parents if required
Referral
- Refer to paediatric surgical team
- Complete nursing and medical documentation for transfer and arrange electronic transfer of any X-rays taken. Ensure you have mother’s name and telephone contact details (including ward details if she is still an inpatient). Surgeon will require verbal telephone consent if an operation is required and an individual with parental responsibility is not able to attend surgical unit at appropriate time
- Inform surgical unit staff when baby ready for transfer. Have available: name, gestational age, weight, ventilatory and oxygen requirements (if applicable) and mother’s name and ward (if admitted)
- Obtain sample of mother’s blood for crossmatch
- sample tube must be clearly hand written and labelled with mother’s name, date of birth, NHS number, and date and time of collection
- complete form
- add baby’s details to ensure it is clear that sample relates to mother of baby being transferred (this information is required by surgical unit blood bank)
USEFUL INFORMATION
Date updated: 2024-02-08