RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
- Rare but potentially fatal neonatal event
- Can occur in the following situations:
- damage to cord before clamping
- massive placental abruption
- massive acute feto-maternal haemorrhage
- subgaleal haemorrhage
- unintended scalpel injury during caesarean section
DEFINITION
- Actual/suspected blood loss with haemodynamic instability or
- Blood loss 2–3 mL/kg/hr
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
Hypovolaemia
- High/increasing heart rate (>160 bpm)
- Low/falling Hb or haematocrit
- Poor peripheral perfusion with slow central capillary refill (>3 sec)
- Low or falling blood pressure [mean blood pressure (MBP) <40 mmHg in a term baby]
- Presence of, or worsening, metabolic acidosis
- Echocardiography (if available) to assess volume status
- small systemic veins and low ventricular filling volumes can indicate hypovolaemia
INVESTIGATIONS
- Crossmatch
- FBC
- PT
- APTT
- Fibrinogen
- U&E
- Ionised calcium
- Blood gases
- If feto-maternal haemorrhage suspected, request maternal Kleihauer test
Hb can be normal due to lack of dilutional effect – do not view as reassuring
IMMEDIATE TREATMENT
Major haemorrhage pathway (MHP)
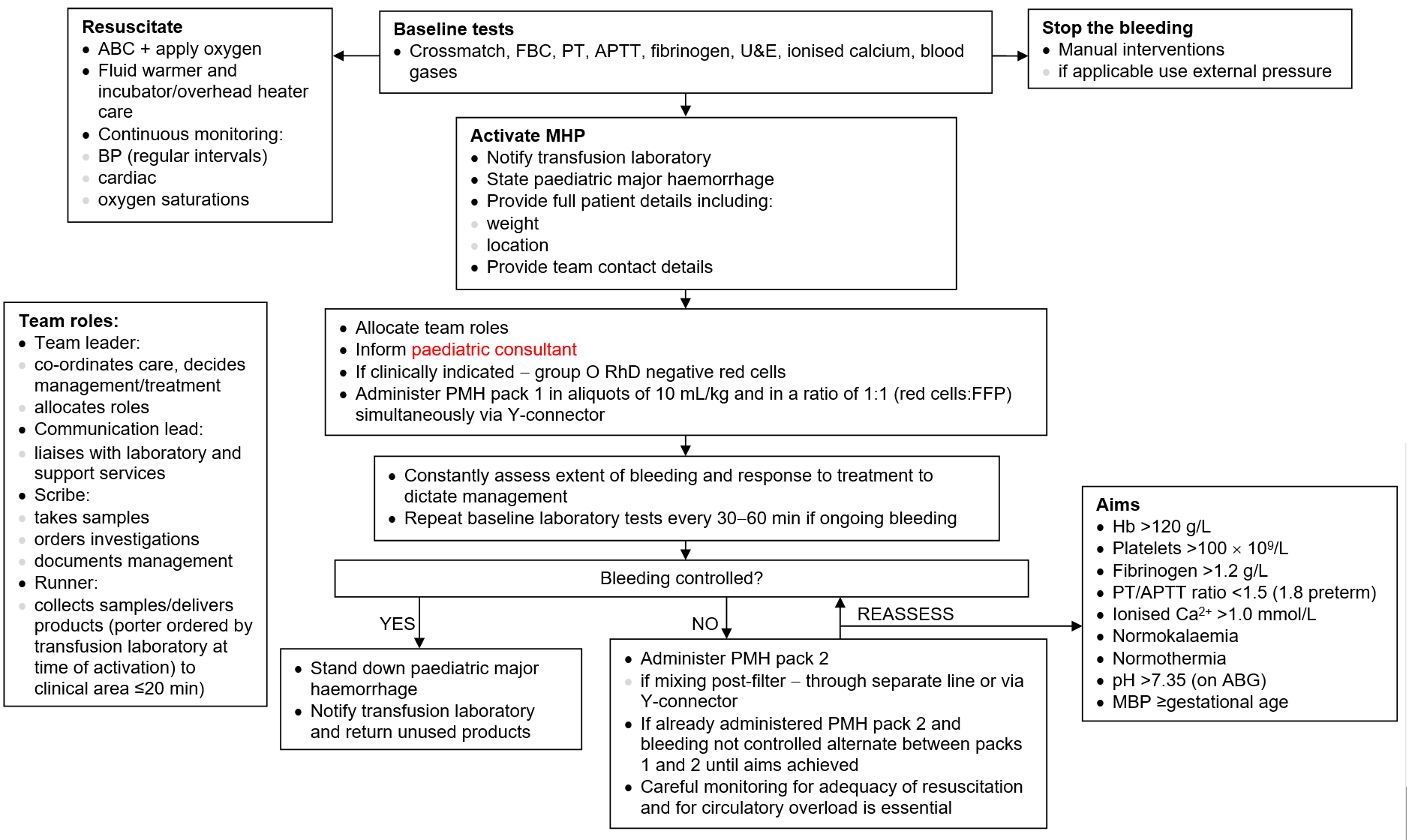
Group O RhD negative blood can be used whilst awaiting massive haemorrhage protocol blood products –
ALWAYS available on labour suite/obstetric theatres
ALWAYS available on labour suite/obstetric theatres
Table 1: Products
| Product | Unit |
|
RBC (20 mL/kg) |
Paediatric (<100 mL) |
|
Plasma (20 mL/kg) |
Neonatal fresh frozen plasma (100 mL) |
|
Platelets (20 mL/kg) |
Paediatric platelets (50 mL) |
|
Cryoprecipitate (10 mL/kg) |
Single donor (40 mL) |
Table 2: Paediatric major haemorrhage pack contents
| Pack 1 | Pack 2 | |
| Packed red cells | ✓ | ✓ |
| FFP | ✓ | ✓ |
| Platelets | ✓ | |
| Cryoprecipitate | ✓ |
- Note: Pack contents –these are not packs that actually exist, but provide a way of thinking through what should be needed in suitable ratios. Many centres will need to design and implement a local protocol between haematology and neonatal teams to plan for this eventuality, based on this structure and flowchart
SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT
- The following may be necessary, discuss with neonatologist:
- elective intubation and ventilation (following resuscitative blood and blood product replacement)
- inotropic support
DISCHARGE AND FOLLOW-UP
- Neurodevelopment follow-up for long-term neurological outcome
Date updated: 2024-01-10