DEFINITION
- Serum sodium >145 mmol/L
- mild: 146–149 mmol/L
- moderate: 150–160 mmol/L
- severe: >160 mmol/L
Most common cause is failure to establish adequate oral intake while attempting breastfeeding
AIM
To prevent/treat hypernatraemic dehydration while encouraging breastfeeding
Other causes of hypernatraemia
- Diarrhoea/vomiting
- Infection and poor feeding
- Renal dysplasia
- Obstructive uropathy
- Diuretic phase following acute kidney injury
- Osmotic diuresis
- Diabetes insipidus
- Idiopathic causes
- Sodium bicarbonate or sodium chloride administration
- Excessive insensible losses in extremely premature babies
- Improperly prepared formula
PREVENTION
Babies at high risk
- Preterm <37 weeks
- Born to primiparous women
- Maternal prolonged second stage of labour >1 hr
- Use of labour medications
- Caesarean section with delayed initiation of feeding
- Cleft lip and/or palate
- Maternal breast characteristics (flat, inverted nipples)/surgery
- Maternal illness, haemorrhage
- Maternal obesity
- Maternal diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Skin conditions that increase insensible water loss
Action
- Identify babies at risk
- Immediate skin-to-skin contact at birth and breastfeed within 1 hr of life
- Offer breastfeeding assistance within 6 hr of life
- Assess baby to ensure feeding adequate
- Ensure baby feeds ≥6 times within 24 hr
- If baby reluctant to feed, express breast milk (see Breast milk expression guideline) and offer by cup or syringe
- Calculate required volume of feeds (see Nutrition and enteral feeding guideline)
- Avoid bottle feeding as far as possible and avoid dummies
- Assess feeding, number of wet nappies and stools using Table
- Avoid early discharge of at-risk babies
- Early reweighing of at-risk babies (at 72–96 hr) with breastfeeding support can reduce severity of hypernatremic dehydration
| Day | Wet nappies | Stool |
| 1–2 | ≥2/day | >1/day |
| 3–4 | ≥3/day | ≥2/day, changing in colour and consistency |
| 5–6 | ≥5/day | ≥2/day, yellow in colour |
|
||
Symptoms and signs
- Irritability/high pitched cry: unsettled during breastfeeding
- Prolonged feeding >45 min
- Demanding <6 feeds in 24 hr
- Reduced urinary frequency
- Delayed change from meconium to transitional stools
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Jaundice
- Lethargy/altered level of consciousness
- Tremor
- Increased tone
- Doughy skin
- Seizures (usually during rehydration)
- Physical examination may be unremarkable
- Usual signs of dehydration (sunken fontanelle, dry mucous membrane and reduced skin turgor) may be absent
Complications
- Venous and arterial thrombosis
- Subdural and cerebral haemorrhage
- Cerebral oedema (especially during rehydration)
- Seizures (especially following rehydration)
- Apnoea and bradycardia
- Cognitive and motor deficits
- Hearing impairment – may be transient
- Hypertension
- Cerebral infarction
- Renal failure
- Death
- Long-term developmental delay
Investigations
- U&E
- Calcium
- Total bilirubin
- Blood glucose
- CRP
- Blood culture
- Paired urinary electrolytes
- If severe, cranial ultrasound
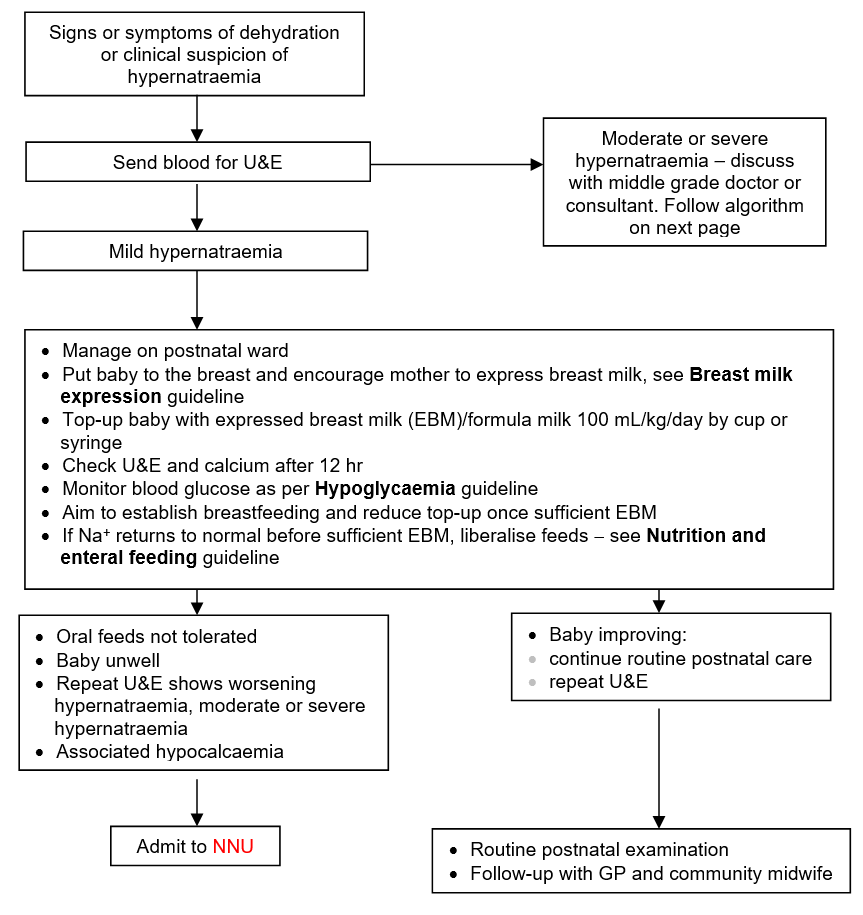
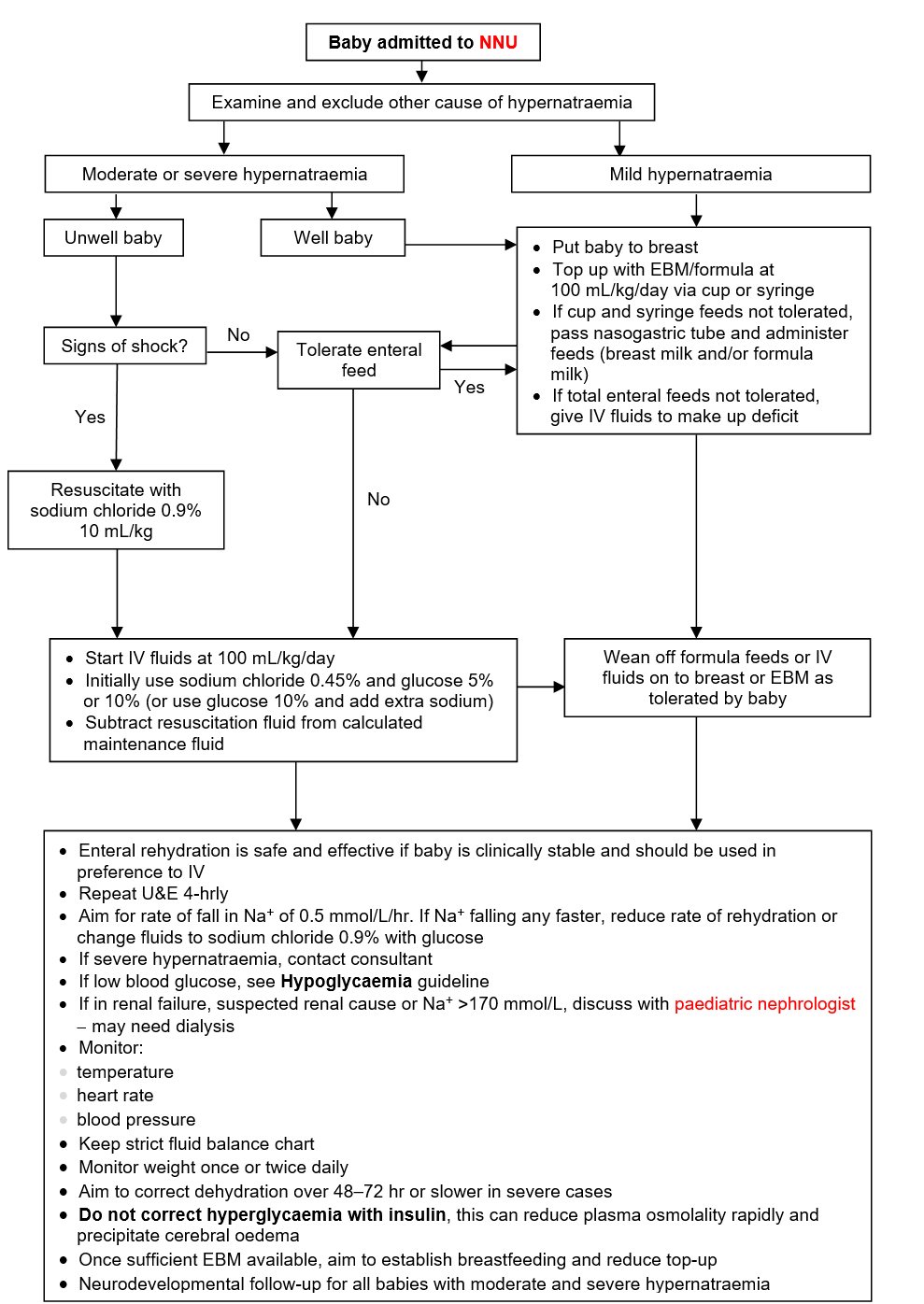
MANAGEMENT
Date updated: 2024-02-05